Introduction
The female chest remains essential because it serves crucial both functional aspects along with aesthetic functions for the body. Breast feeding functions form one essential role but chest tissue additionally reflects female characteristics and shapes overall body perception. Knowledge about the structure and functioning of breasts together with appropriate care practices forms a fundamental requirement for overall wellness.
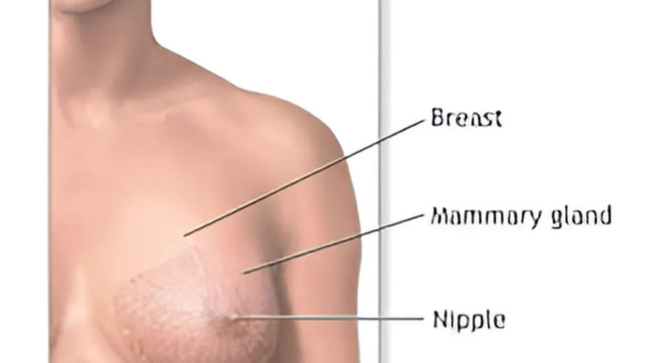
Breast Anatomy
The human breast contains three fundamental tissue types which include lobules as well as adipose tissue along with fibrous structures. The main components include:
Mammary Glands – Responsible for milk production.
Milk Ducts are responsible for transferring milk through the body to reach the nipple.
Fat Tissue – Determines breast size and shape.
The nipples together with the areola maintain their vital purpose as the gateways for breastfeeding.
Ligaments and Muscles – Provide support and shape.

Breast Development
The initial development ofbreast occurs during puberty since hormonal alterations take effect. Faultless development of the breasts occurs when estrogen and progesterone operate together to promote growth during adulthood. Genetics combined with hormones and lifestyles determine variations in chest sizes along with their shapes.
Function of the Breast
Milk production through breasts functions as their principal biological purpose because it enables nursing of babies. The process of lactation involves:
Post-childbirth milk production happens because of hormonal influences.
The mammary glands store milk before its time for use.
Newborns receive milk when the milk ejection process sends the liquid through the ducts during breast feeding.

Common Breast Changes
Breasts experience different modifications during individual lifespan because of three factors:
Puberty – Initial growth and development.
Pregnancy – Enlargement and milk production.
Menopause – Reduction in size and firmness due to hormonal decline.
Age brings about two changes which lead to declining elasticity and density.
Breast Health Care
Proper care is essential for maintaining overall health. Key practices include:
- Regular Self-Exams – Detect lumps or unusual changes early.
- Healthy Diet – Supports tissue and hormonal balance.
- Exercise – Improves circulation and muscle support.
- Proper Bra Support – Prevents strain and discomfort.
- Moisturizing and Massage – Keeps skin supple and firm.
Common Breast Problems
Several conditions can affect health, including
- Breast Pain (Mastalgia) – Can result from hormonal fluctuations.
- Fibrocystic Breasts – Benign lumps caused by hormonal changes.
- Breast Infections – Often occur during breastfeeding.
- Nipple Discharge – May indicate hormonal imbalances.
Breast Cancer Awareness
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers in women. Early detection & preventive measures are crucial. Important steps include
- Regular Mammograms – Recommended for women over 40.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices – Diet, exercise, and stress management.
- Avoiding Risk Factors – Limiting alcohol and smoking.
Breast Enhancement Options
Some individuals seek to enhance their size for personal or cosmetic reasons. Options include:
- Natural Methods – Diet, exercise, and massage.
- Breast Augmentation – Surgical procedures like implants.
- Fat Transfer – Using body fat to increase volume.
Psychological Impact
Breast size and shape can impact self esteem and body image. Society often places emphasis on appearance, affecting confidence levels. Embracing natural body changes & making informed choices contribute to self acceptance.
Conclusion
Breasts serve vital functions in the female body from breast feeding to aesthetics. Understanding their anatomy, changes, & proper care helps maintain health & confidence. Regular checkups & self care practices ensure long term well being & prevent potential health issues.